Erreur de format d'e-mail
emailCannotEmpty
emailDoesExist
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd

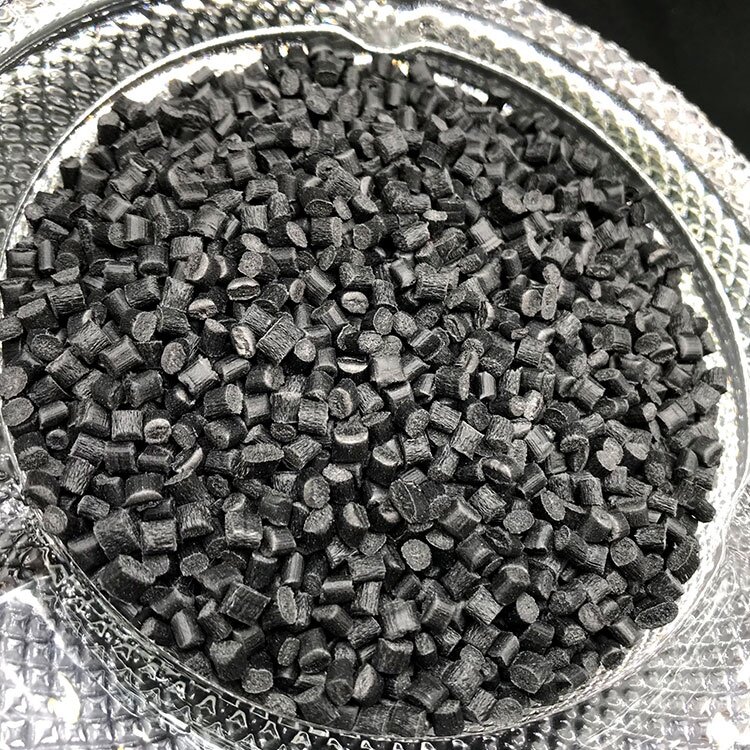
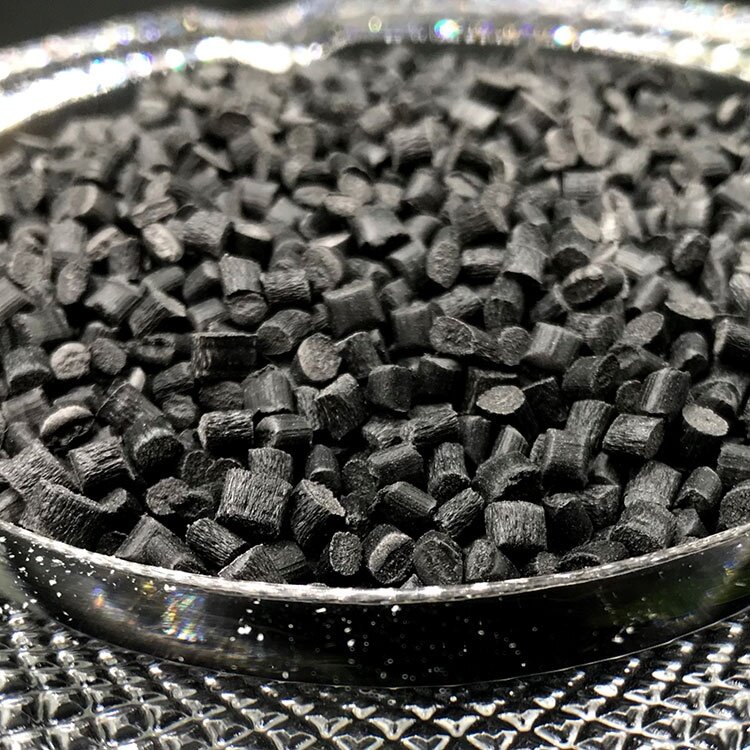
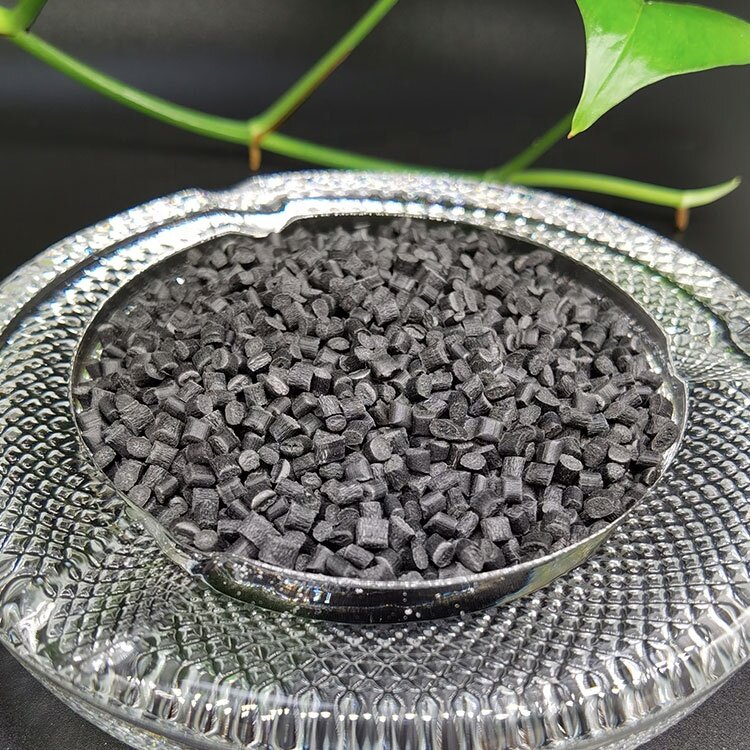
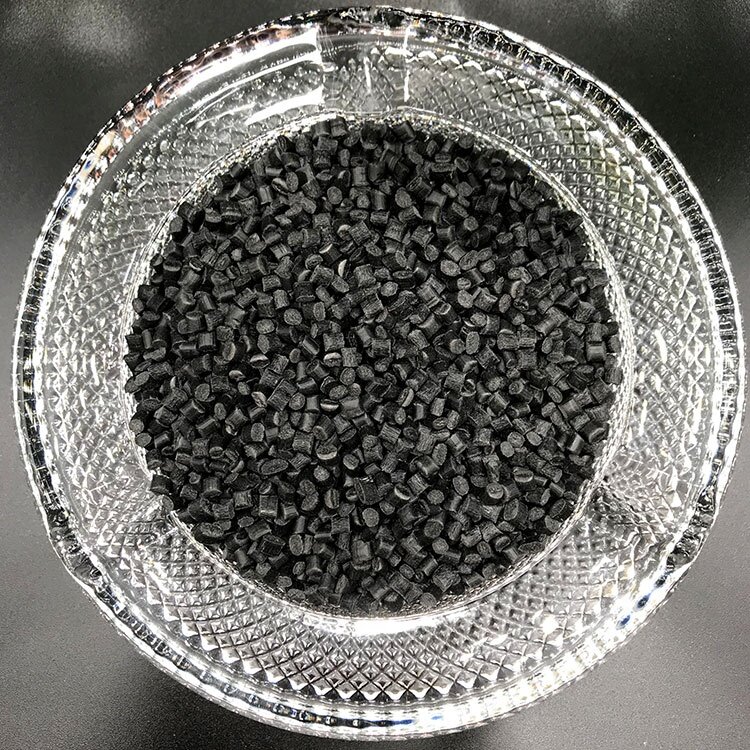
PA6 GF10M20 F07100620
Glass Filled: 10%
Mineral Filled: 20%
(Custom materials available according to your Technical Data Sheet)
- Les détails du produit
-
Download

Customizable Materials Available:
- Color (Customization of plastic pellet color according to your requirements.)
- Flame retardant grade (Let us know which flame retardant level you need: 0.8mm-3.0mm HB, V0, V1, V2, 5VA, 5VB)
- Glass fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- Carbon fiber reinforcement material (10%-50% availability)
- UV resistance property (Tell us the application scenarios or UV resistance level of the materials )
- Other materials can also be customized ( Just need to provide your Technical Data Sheet. )
Technical Data Sheet of PA6 GF10M20 F07100625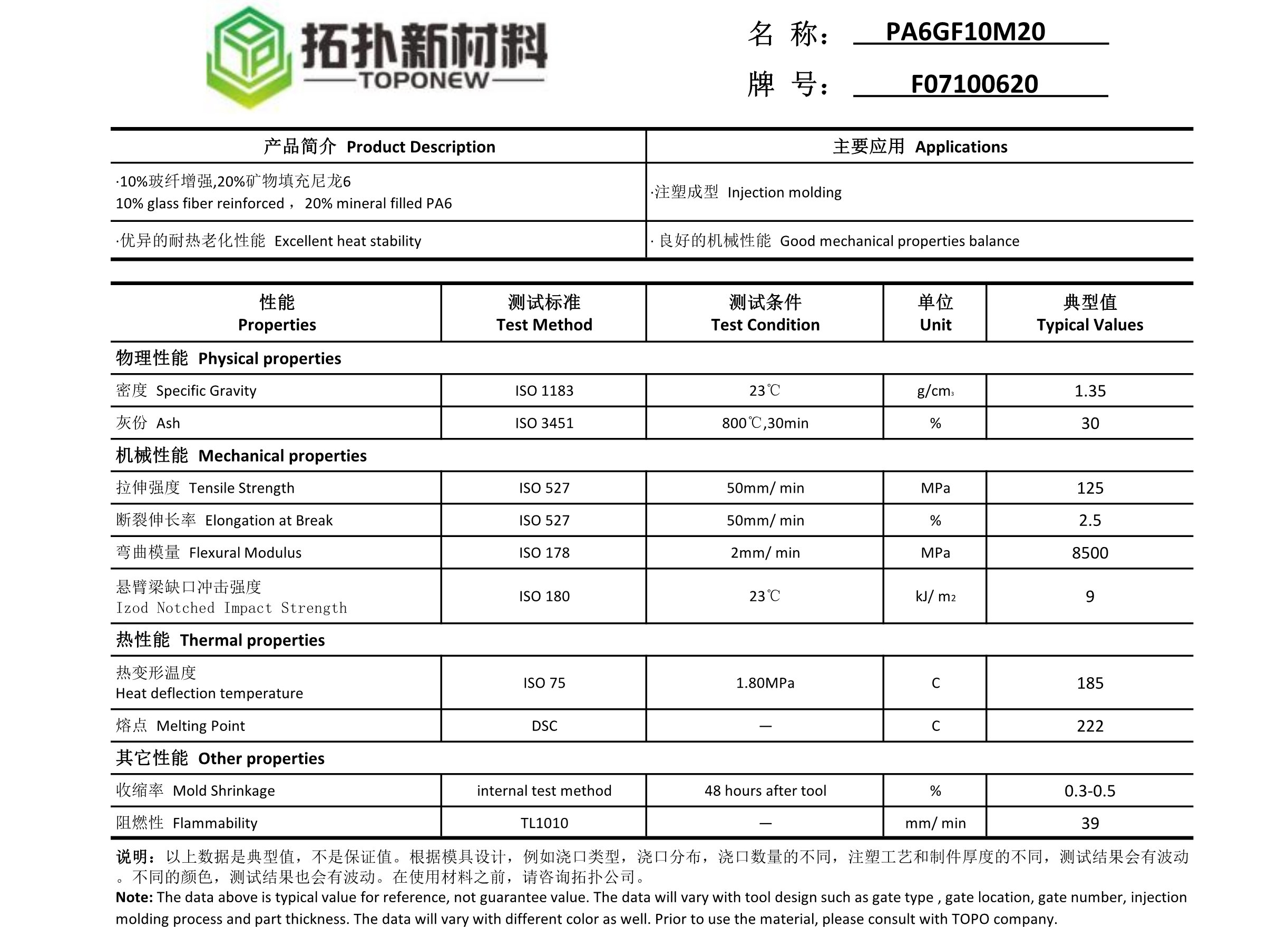
Mineral Filled PA6, also known as mineral filled Nylon 6, is a modified form of Nylon 6 that incorporates mineral fillers into its composition. These mineral fillers, such as mica, or other reinforcing materials, are added to enhance the mechanical properties and performance of the material.
Mineral filled PA6 offers several advantages over traditional unfilled Nylon 6. The addition of mineral fillers significantly improves the strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability of the material. It enhances the material's resistance to impact, abrasion, and wear, making it suitable for applications requiring higher durability and robustness.
The presence of mineral fillers also improves the thermal conductivity and reduces the coefficient of expansion of the material. This makes mineral filled PA6 well-suited for applications where heat dissipation and dimensional stability are important considerations.
Another advantage of mineral filled PA6 is its ability to achieve improved surface finishes. The incorporation of mineral fillers can enhance the material's flow characteristics and reduce shrinkage, resulting in smoother and more aesthetically appealing molded parts.
Due to its enhanced mechanical properties, mineral filled PA6 finds applications in various industries. It is commonly used in the automotive industry for the manufacturing of high-strength structural components, such as engine components, intake manifolds, and under-the-hood parts. It is also utilized in electrical and electronics applications where durability, dimensional stability, and heat resistance are crucial.
Overall, mineral filled PA6 offers a combination of improved mechanical performance, enhanced thermal properties, and superior surface finishes. Its versatility makes it a popular choice for demanding applications across different industries.
Q & A
1. What is mineral filler in plastic?
Mineral fillers are inert, inorganic materials that are added to plastics to modify or enhance various properties of the plastic material. These fillers are derived from natural sources such as minerals and ores. Some common types of mineral fillers include:
-
Talc: Talc is a naturally occurring mineral used as a filler in plastics to improve stiffness, dimensional stability, and heat resistance. It also provides a smooth surface finish and can contribute to increased impact strength.
-
Calcium Carbonate: Calcium carbonate, often derived from limestone or marble, is used as a filler in plastics to improve stiffness, impact resistance, and dimensional stability. It can also reduce costs by displacing a portion of more expensive polymer.
-
Kaolin (China Clay): Kaolin is a fine white clay mineral used in plastics to improve stiffness, tensile strength, and surface finish. It can also help to reduce shrinkage and warpage in molded parts.
-
Mica: Mica is a mineral filler that can improve the thermal and electrical properties of plastic materials. It is commonly used in applications where heat resistance and electrical insulation are important.
-
Barium Sulfate: Barium sulfate is used as a filler in plastics to increase density, enhance flame retardancy, and improve impact strength. It is often used in applications where high density and fire resistance are required.
The addition of mineral fillers to plastics can help optimize material properties, reduce costs, and improve the overall performance of the plastic material in various applications. Each type of mineral filler has its own set of properties and benefits, so the selection of the filler depends on the specific requirements of the end product.
Mineral-filled polypropylene, which is polypropylene material that has been reinforced with mineral fillers such as talc, calcium carbonate, or mica, exhibits several enhanced properties compared to unfilled polypropylene. Some of the key properties of mineral-filled polypropylene include:
-
Improved Mechanical Properties: The addition of mineral fillers can increase the stiffness, strength, and impact resistance of polypropylene. This results in materials that are better able to withstand mechanical stresses and impacts.
-
Reduced Shrinkage and Warpage: Mineral fillers help to reduce the shrinkage and warpage of polypropylene parts during processing and cooling. This can lead to improved dimensional stability and tighter tolerances in molded components.
-
Enhanced Heat Resistance: Mineral fillers can improve the heat resistance of polypropylene, making it more suitable for applications requiring exposure to higher temperatures.
-
Improved Surface Finish: Mineral fillers can help improve the surface finish of polypropylene parts, resulting in a smoother and more aesthetically pleasing appearance.
-
Increased Modulus: The addition of mineral fillers can increase the modulus of mineral-filled polypropylene, making it stiffer and more rigid.
-
Cost Efficiency: By incorporating mineral fillers, manufacturers can achieve cost savings by replacing a portion of the more expensive polymer with the less expensive filler material.
-
Reduced Density: In some cases, mineral fillers can help reduce the density of polypropylene compounds while maintaining or even improving mechanical properties.
Overall, mineral-filled polypropylene compounds offer a balance of improved mechanical properties, dimensional stability, heat resistance, and cost efficiency, making them well-suited for a wide range of applications in industries such as automotive, consumer goods, packaging, and construction.
Download
-
TOPONEW PA6GF10M20 .pdf
Download TOPONEW PA6GF10M20 .pdf










